How you can use this image
This image is available to be shared and re-used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives licence (CC BY-NC-ND).
You can reproduce this image for non-commercial purposes and you are not able to change or modify it in any way.
Wherever you reproduce the image you must attribute the original creators (acknowledge the original artist(s) and the person/organisation that took the photograph of the work) and any other rights holders.
Review our guidance pages which explain how you can reuse images, how to credit an image and how to find more images in the public domain or with a Creative Commons licence available.
DownloadNotes
Add or edit a note on this artwork that only you can see. You can find notes again by going to the ‘Notes’ section of your account.
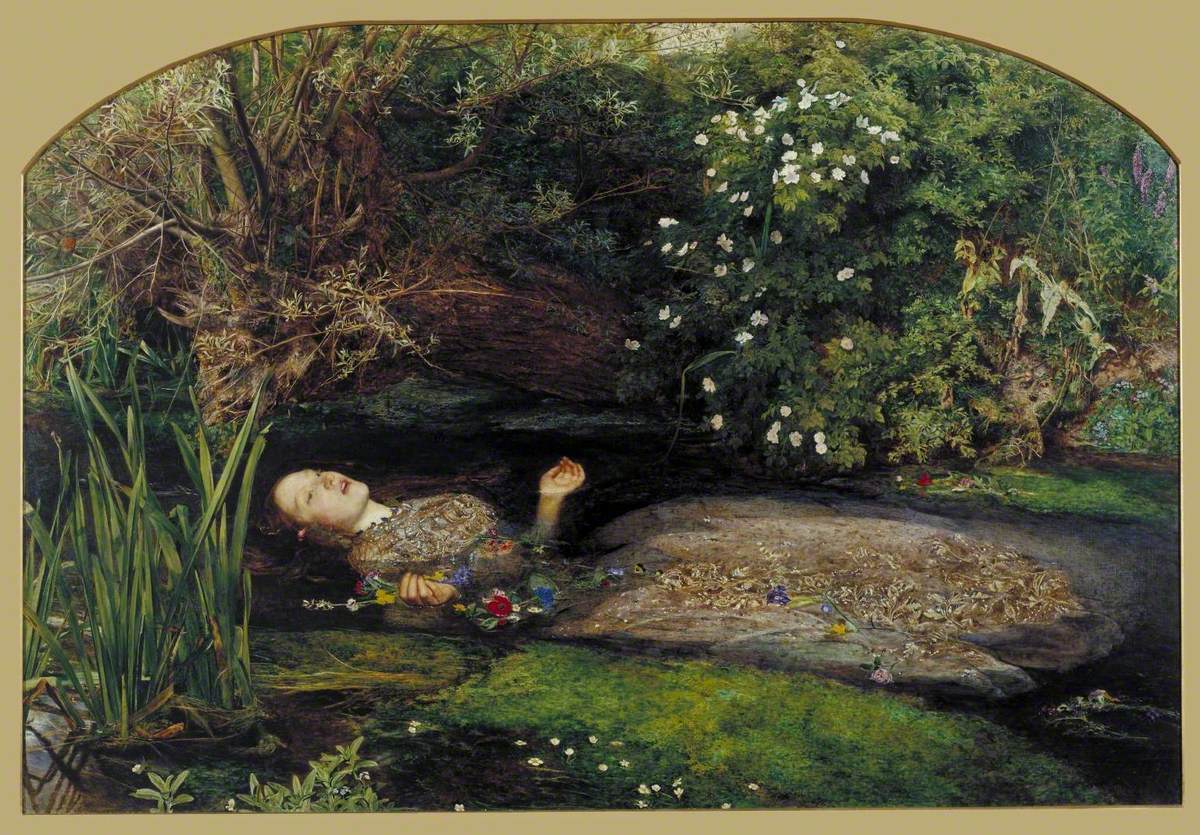
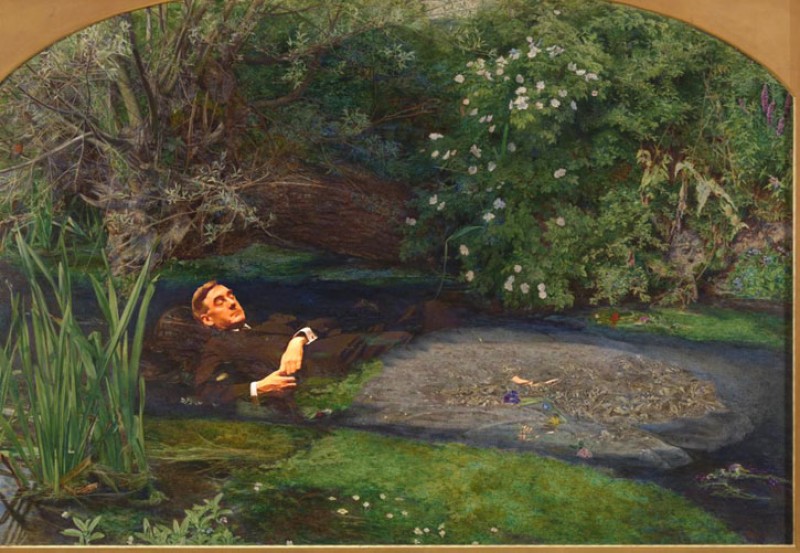
The scene depicted is from Shakespeare's Hamlet, Act IV, Scene vii, in which Ophelia, driven out of her mind when her father is murdered by her lover Hamlet, drowns herself in a stream: 'There, on the pendent boughs her coronet weeds Clambering to hang, an envious sliver broke; When down her weedy trophies and herself Fell in the weeping brook. Her clothes spread wide, And, mermaid-like, awhile they bore her up; Which time she chanted snatches of old tunes, As one incapable of her own distress, Or like a creature native and indued Unto that element; but long it could not be Till that her garments, heavy with their drink, Pull'd the poor wretch from her melodious lay To muddy death'. Shakespeare was a favourite source for Victorian painters, and the tragic-romantic figure of Ophelia from Hamlet was an especially popular subject, featuring regularly in Royal Academy exhibitions. Arthur Hughes exhibited his version of her death scene in the same year as this picture was shown (Manchester Art Gallery).
The plants, most of which have symbolic significance, were depicted with painstaking botanical detail. The roses near Ophelia's cheek and dress, and the field rose on the bank, may allude to her brother Laertes calling her 'rose of May'. The willow, nettle and daisy are associated with forsaken love, pain, and innocence. Pansies refer to love in vain. Violets, which Ophelia wears in a chain around her neck, stand for faithfulness, chastity or death of the young, any of which meanings could apply here. The poppy signifies death. Forget-me-nots float in the water. Millais wrote to Thomas Combe in March 1852: 'Today I have purchased a really splendid lady's ancient dress – all flowered over in silver embroidery – and I am going to paint it for "Ophelia". You may imagine it is something rather good when I tell you it cost me, old and dirty as it is, four pounds' ('J. G. Millais I', p.162). Ophelia was part of the original Henry Tate gift to the Tate Gallery.
Further reading: John Guille Millais, 'The Life and Letters of Sir John Everett Millais', 1899, I, pp.116–120, 123, 129–131, 144–147, 151, 162–163 Leslie Parris (ed.), 'The Pre-Raphaelites', exhibition catalogue, Tate Gallery, London 1984, reprinted 1994, pp.96–98, reproduced in colour Terry Riggs February 1998
Title
Ophelia
Date
1851–2
Medium
Oil on canvas
Measurements
H 76.2 x W 111.8 cm
Accession number
N01506
Acquisition method
Presented by Sir Henry Tate 1894
Work type
Painting
Inscription description
date inscribed
Tate Britain
Millbank, London, Greater London SW1P 4RG England
Stories
-
 Eight muses who inspired art history's masterpieces
Eight muses who inspired art history's masterpiecesRuth Millington
-

-
 Tragic love: representing the downfall of Shakespeare's Ophelia
Tragic love: representing the downfall of Shakespeare's OpheliaChloe Esslemont
-

-

-
 2016 as told through the nation's art collection
2016 as told through the nation's art collectionMolly Tresadern
-
 Why look at Old Masters?
Why look at Old Masters?Nicola Jennings
-
 Ten paintings of female poets in UK collections
Ten paintings of female poets in UK collectionsAna Sampson
-
 Art Matters podcast: reflecting 'madness' in art
Art Matters podcast: reflecting 'madness' in artFerren Gipson
-

-

-
 Who were the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood?
Who were the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood?Andrew Shore
-
 The art of lying: reclining figures through history
The art of lying: reclining figures through historyLydia Figes and Andrew Shore
-
 Art Matters podcast: the art of Disney animation
Art Matters podcast: the art of Disney animationFerren Gipson








